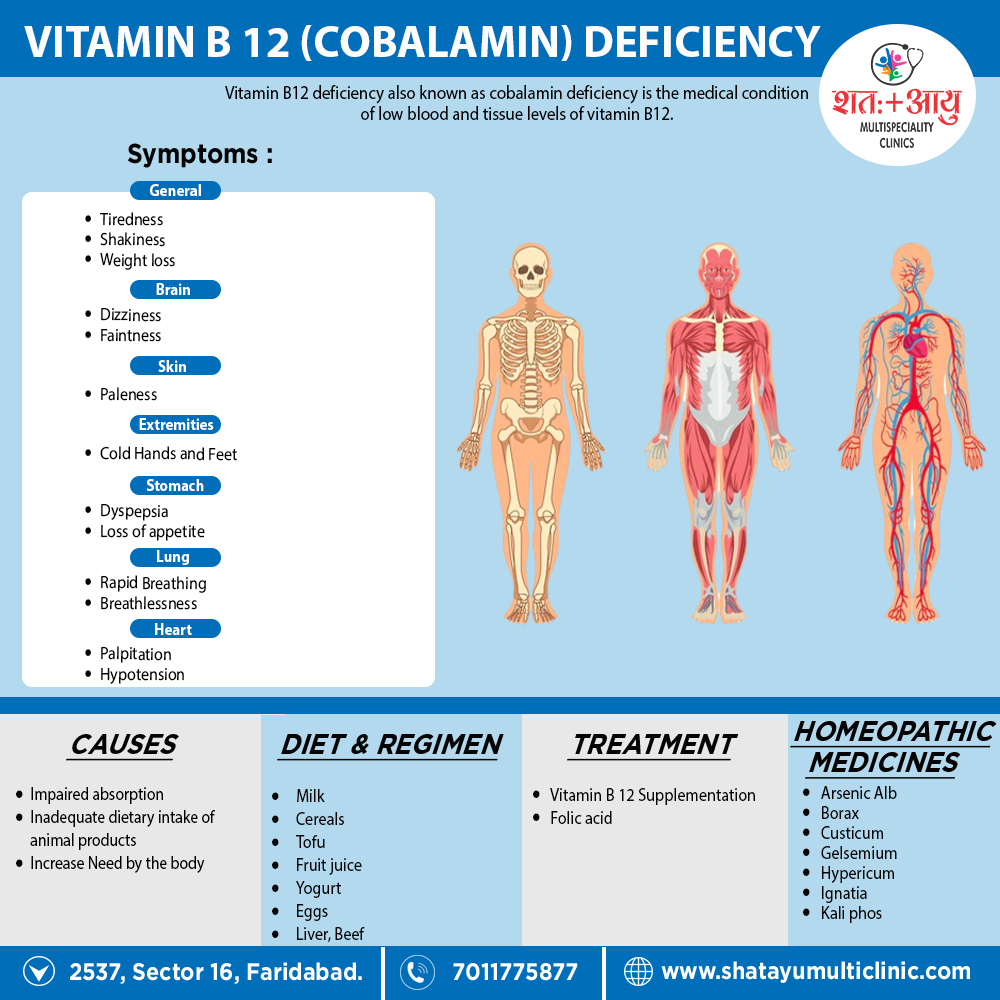
Homoeopathic Treatment for Vitamin B 12 Deficiency
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis, which includes the medical history of the patient, physical and mental constitution, family history, presenting symptoms, underlying pathology, possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions. A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease is not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness are also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology is not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can be greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications are also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Homeopathic Medicine for Vitamin B 12 Deficiency :
Arsenic Album
To Manage Weakness, Tiredness i.e.
- Arsenic Album is a very effective homeopathic medicine to manage weakness, tiredness. In persons needing it weakness is felt from doing even least exertion. Mostly they have weakness in the night hours.
- Intense weakness is there in limbs that forces the person to lie down. They are also very anxious and restless, with a desire to move constantly.
- Apart from above, it is well-indicated medicine to manage tingling sensation felt in the fingers. Weakness, numbness in the feet is yet another symptom calling its use.
Aloe
For Managing Diarrhea i.e.
- This medicine is prepared from gum of the plant Aloe Socotrina. It belongs to family liliaceae. It is one of the best medicines in homeopathy to manage diarrhoea.
- In cases needing it there is passage of lumpy, watery stool. There is a desire to pass soon after eating or drinking. Urgency to pass stool is also present.
- A constant bearing down sensation is felt in rectum. The main indication for using it is morning diarrhea that makes a person rush out of bed and go to pass stool immediately upon rising in morning. [2]
Borax
For Managing Mouth Ulcers i.e.
- In cases needing it, the ulcers can be present inside of the cheek or tongue. The ulcers are painful and tender. They also tend to bleed easily.
- Excessive heat and dryness of mouth can felt along with these features.
Custicum
For Muscle Weakness and Problem with Balance and Coordination i.e.
- It is a prominent medicine with marked action on the muscles. It is a top-grade medicine to help cases in which muscle weakness is prominent.
- Another major indication for using it is the problem with balance and coordination that cause unsteady walking and easy falling. It also works well to manage numbness in the hands.
Gelsemium
To Manage Exhaustion and Dizziness i.e.
- A natural medicine prepared from the bark of the root of plant Gelsemium Sempervirens commonly known as yellow jasmine.
- This plant belongs to family Loganiaceae. This medicine helps manage complaints of exhaustion and dizziness. In cases requiring it dullness and drowsiness is also present.
- There is also a desire to lie down at all times. Dizziness may occur while walking. Also indicated for managing cases in which there occurs confusion of mind, thinking difficulty and problem in concentration
Hypericum
For Tingling Sensation in Limbs i.e.
- Hypericum prepared from a plant Hypericum Perforate also known by the name of St. John’s Wort. This plant belongs to family hypericaceae.
- Use of this medicine if highly recommended to manage tingling and burning sensation in the limbs. Numbness in limbs may also be there in some cases.
Ipecac
For Managing Nausea and Vomiting i.e.
- Ipecac medicine prepared from the dried root of plant Ipecacuanha belonging to the family rubiaceous. It is very useful to manage nausea and vomiting.
- The nausea can be constant in persons needing it. Vomiting may occur of watery fluids, food or bile. The nausea may not get better even after vomiting.[2]
Ignatia
For Managing Depression i.e.
- It is a very beneficial medicine in homeopathy for managing depression. People needing it feel sad all the time. This is accompanied with weeping also brooding spells.
- People who need this medicine do not wish to meet other people. They may also have dullness and weakness of mind.
Kali Phos
To Manage Fatigue, Memory Weakness, Numbness, Prickling i.e.
- It is an important medicine to help cases in which fatigue is present on both mental and physical spheres. Doing the slightest amount of work seems daunting.
- They have low energy levels.
It is also a suitable medicine for managing weakness of memory, forgetfulness, dullness of mind. Other than these, it is also a significant medicine for managing irritability also depression.
- In such cases sadness, gloominess, is present. Other symptoms that can attend are weariness of life, negative thoughts in mind and fear of death. Lastly, it works well when there is numbness or prickling sensation in the hands and feet.[2]
Lycopodium
To Manage Gas i.e.
- Lycopodium prepared from plant Lycopodium Clavatum commonly known as club moss that belongs to the family lycopodiaceae.
- This medicine works well in cases where excessive gas production is there. Furthermore, It results in abdominal bloating. After eating any food there occurs bloating. Abdominal pain also occur if the gas is not passed.
Merc Sol
To Manage Inflammation of Tongue and Mouth Ulcers i.e.
- It is a highly valuable medicine for managing tongue inflammation. In such cases there is intense redness of tongue accompanied with pain.
- The pain is usually pricking in nature. Burning sensation can also occur with this.
Next, it is very effective for cases of mouth ulcers. The ulcers can occur on the tongue, gums, inside cheeks when it is needed. These are dirty looking with undefined borders.
- Excessive salivation, metallic taste in mouth and offensive breath are some general symptoms that can appear with above complaints.
Picric Acid
For Managing Pin and Needle Sensation i.e.
- This is a beneficial medicine for managing pin and needle sensation in the limbs. Weakness and tiredness in the whole body especially in the limbs can also be present in cases needing it.
- Some other indications for using this medicine include weakness of memory, forgetfulness and mental fatigue after doing least intellectual work.
Sarcolacticum Acidum
For Extreme Fatigue, Prostration i.e.
- It yet another indicated medicine for managing fatigue, prostration. For using it the muscle weakness is present in the back, neck and shoulders.
- It also felt in limbs when climbing stairs. Lastly weakness is felt in arms as if it has no strength in them.
Zincum Met
To Manage Numbness and Tingling i.e.
- Zincum Met is also very useful medicine for managing numbness and tingling sensation.
- Sometimes formation sensation is felt in feet and legs. Muscle weakness in the limbs may also be present [2]