Overview
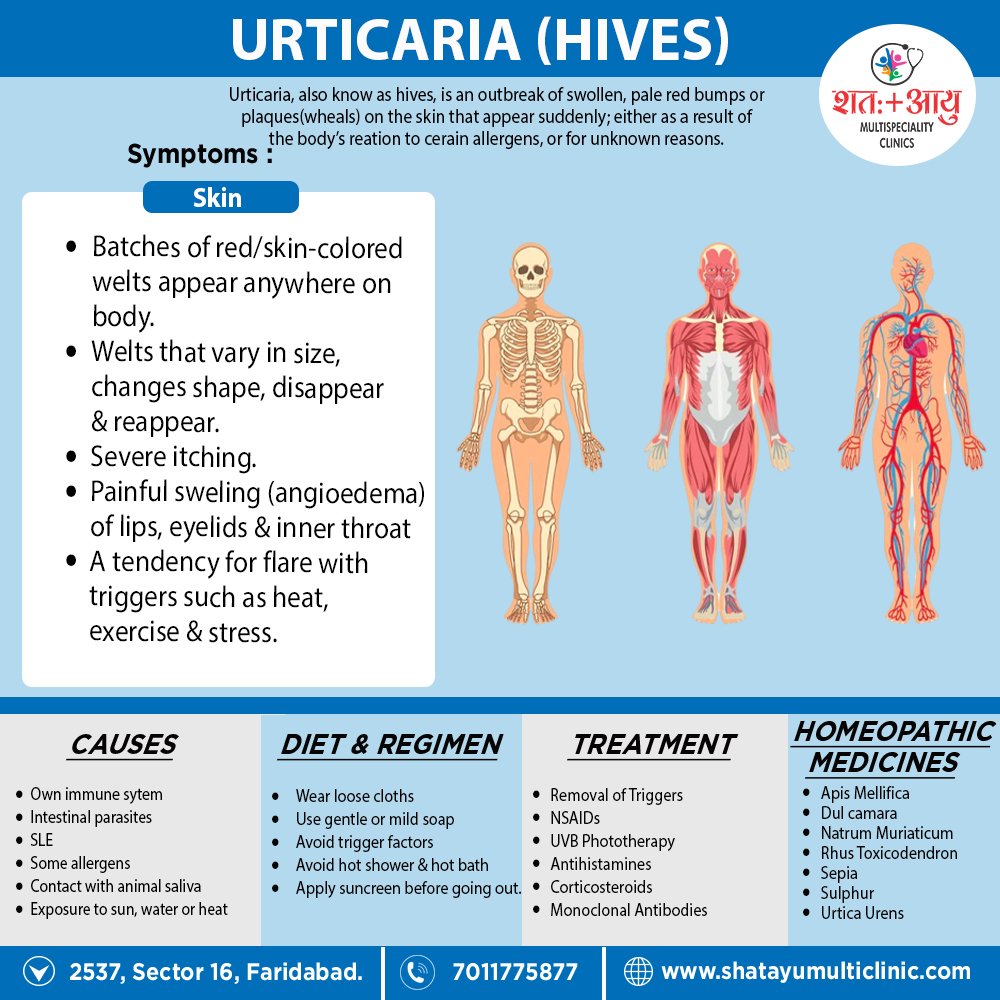
It is also known as urticaria, welts, weals, or nettle rash.
Generalized Urticaria
- When an allergic reaction occurs, the body releases a protein called histamine.
- When histamine is release, the tiny blood vessels known as capillaries leak fluid.
- Moreover, The fluid accumulates in the skin and causes a rash.
- It is not contagious. [2]
- Hives usually cause itching, but may also burn or sting.
- They can appear anywhere on the body.
- Besides this, Hives vary in size (from a pencil eraser to a dinner plate), and may join together to form larger areas known as plaques.
- They can last for hours, or up to one day before fading.
- Urticaria (‘hives’) is cause by localise dermal oedema secondary to a temporary increase in capillary permeability.
- Lastly, If oedema involves subcutaneous or submucosal layers, the term angioedema is use.
Other factors
- Angioedema is similar to hives, but the swelling occurs beneath the skin instead of on the surface.
- Angioedema is characterize by deep swelling around the eyes and lips and sometimes of the genitals, hands, and feet.
- It generally lasts longer than hives, but the swelling usually goes away in less than 24 hours.
- Rarely, angioedema of the throat, tongue, or lungs can block the airways, causing difficulty breathing & may become life threatening. [3]
- Acute urticaria may associate with angioedema of the lips, face, tongue, throat and, rarely, wheezing, abdominal pain, headaches and even anaphylaxis.
- Urticaria present for less than 6 weeks is considered to be acute, also chronic if it continues for more than 6 weeks.
- Individual weals last for less than 24 hours; additionally if they persist, urticarial vasculitis needs to be considered. [1]