Definition of Shoulder pain
Shoulder pain is defined as Physical discomfort of the shoulder, including the joint itself or the muscles, tendons and ligaments that support the joint. [1]
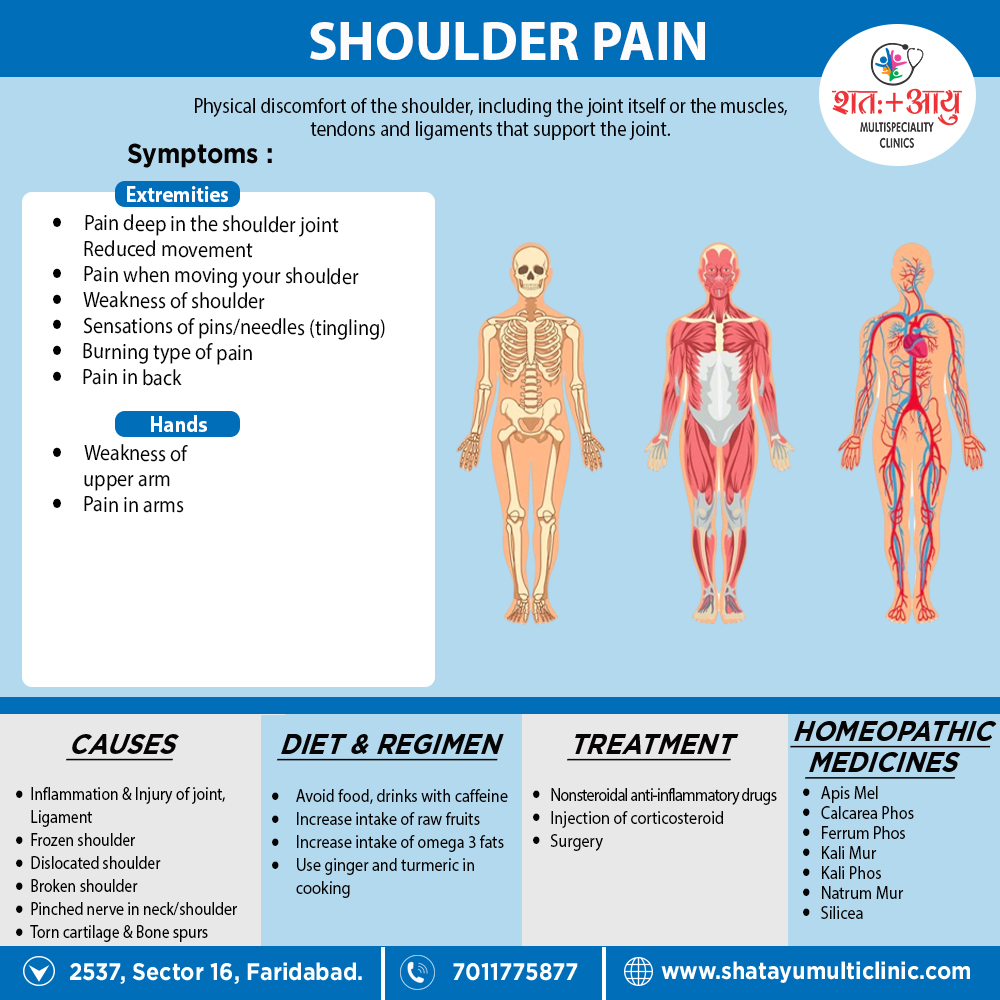
Shoulder pain is defined as Physical discomfort of the shoulder, including the joint itself or the muscles, tendons and ligaments that support the joint. [1]
During the evaluation of shoulder disorders, the examiner should carefully note any history of trauma, fibromyalgia, infection, inflammatory disease, occupational hazards, or previous cervical disease.[2]
Shoulder pain may originate in the Glenohumeral or acromioclavicular joints, sub acromial (subdeltoid) bursa, periarticular soft tissues (e.g., fibromyalgia, rotator cuff tear/tendinitis), or cervical spine. [2]
Other causes of shoulder pain include:[1]
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
which includes
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
It is defined as Physical discomfort of the shoulder, including the joint itself or the muscles, tendons and ligaments that support the joint.
References: