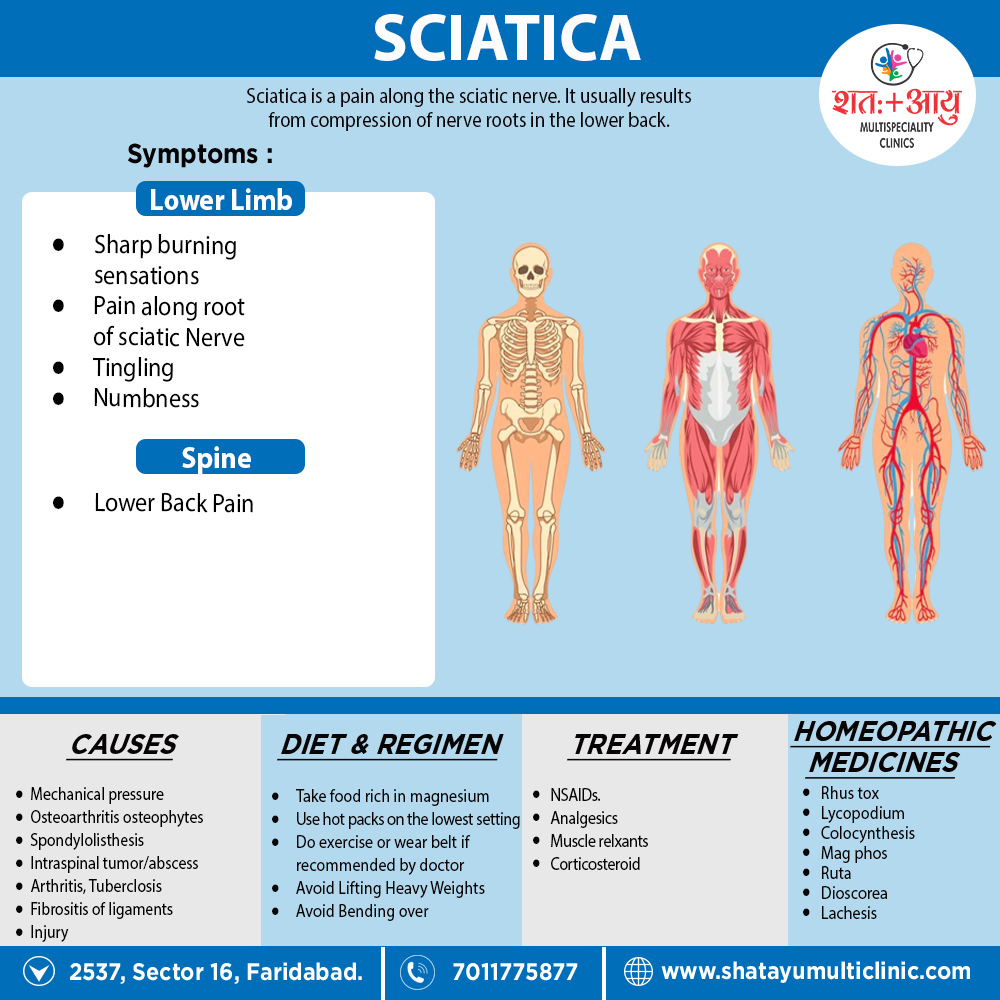
Homeopathic Treatment of Sciatica
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Sciatica
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy, potency and repetition of dose by Homeopathic doctor.
So, here we describe homeopathic medicine only for reference and education purpose. Do not take medicines without consulting registered homeopathic doctor (BHMS or M.D. Homeopath).
Medicines:
-
Rhus tox:
- Generally, Aching pains in legs must change position every moment.
- Sciatica with tearing, drawing pain also burning pain hip-joint to hamstrings.
- Tingling in feet, stiffness, tension in leg, lameness. Additionally, Cramps buttocks, thighs and calves.
- Worse – cold, damp weather, at night, sleep, lifting, overexertion, during rest, lying on back, lying especially on right side.
- Better – dry, warm weather, warmth, walking, rubbing, change of position.
-
Lycopodium:
- Sometimes most useful in chronic cases where there is fine burning or stinging pains, also tearing, drawing, jerking pains which are aggravation from rest.
- Lameness, cramps in calves and toes in bed at night. Restless limbs preventing sleep.
- Worse – right side, cannot lie specifically on painful side, morning on waking, rising from seat, heat or warmth of a room, bed, before midnight, rest. On the other hand, Better – motion.
-
Colocynthis:
- Typifies the sciatica due to nerve changes with no special inflammatory conditions attending it.
- Contraction of muscles. Cramp-like pain in hip, lies on affected side; pain from hip to knee.
- Pain drawing, tearing. Pain down right thigh, muscles and tendons feel too short.
- Numbness with pains. Pains may come and leave suddenly
- Worse – gentle touch, motion, cold. Whereas, Better – pressure, heat.
-
Mag phos:
- Cramping of muscles with radiating pains. Neuralgic pain Amelioration warmth. Cramps in calves.
- Feet very tender. Spasmodic pain. Sudden pain. Pains in lower limbs on alternate sides.
- Worse – especially right side, cold, touch, night. On the other hand, Better – warmth, bending double, pressure, friction. [1]
-
Ruta:
- Deep-seated pain as if in marrow of bone; worse specifically at rest; pain compels patient to walk about constantly during paroxysm. After injuries, contusions, etc.
-
Dioscorea:
- Pain in right leg from point of exit of sciatic nerve, felt only when moving the limb or when sitting up (rising from lying to sitting posture).
- That means: aggravated by walking or moving the limb and entire relief when sitting still. A few distinct pointers
- Pains radiate downwards
- Frequent shooting pains from one part to another.
- Pains of all sorts which are unbearable.
- Pains dart about (go away suddenly and reappear in a different part of the affected limb)
-
Lachesis:
- Pain constantly changes locality, now in head, now in teeth, now in sciatic nerve, attended with nervousness and palpitation of heart.[5]