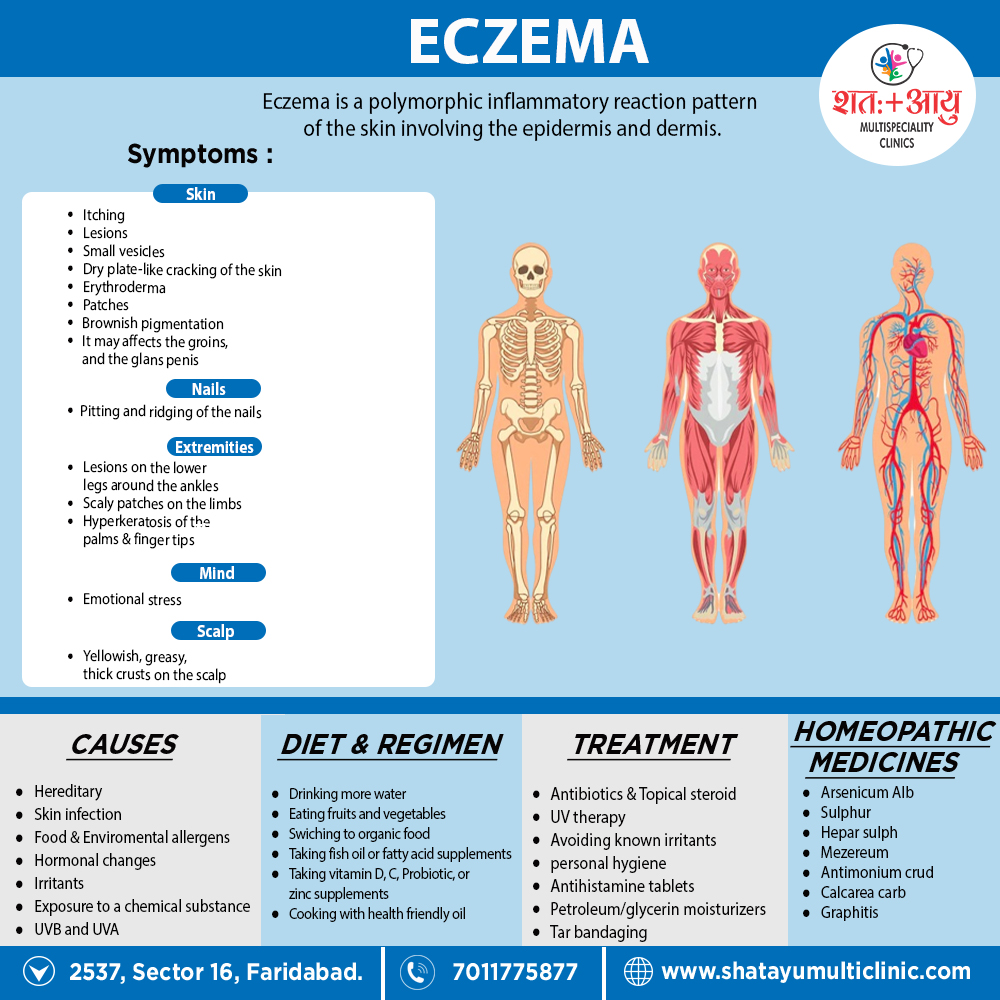
Homeopathic Treatment of Eczema
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Homoeopathic Approach:
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines are selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis, which includes the medical history of the patient, physical and mental constitution, family history, presenting symptoms, underlying pathology, possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) is also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions. A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’. The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease is not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness are also looked for.
Now a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition. The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology is not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can be greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications are also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Medicine:
Arsenicum Alb:
- People who need this remedy usually are anxious, restless and compulsively neat and orderly.
- Chronic eczema; eruption upon scalp and face dry and scaly, or pimples and vesicles upon face with acrid, sometimes foetid, discharge and intense burning itching, the same on likes and genitals.
- Margin of hair, itching and burning, by scratching, followed by bleeding.
- Indigestion with burning pain and a general feeling of chilliness.
- Harsh, dry, rough skin in papers not affected by the eruption; emaciation from disturbances in vegetative sphere; emaciation of urine shows deficiency of urea.[5]
- Aggravation at night and in cold air, Amelioration from warmth. Barnlike, scaly eruption, on forehead.
Asterias Rubens:
- Eczema on thighs, legs, ankles and instep.
- Itching vesicles break and form small ulcers which spread superficially.
- Scrofulous and sycotic constitutions.[5]
Calcarea Carb:
- This remedy is suited to people who are chilly with clammy hands and feet, and tend to develop eczema and cracking skin that is worse in the wintertime.
- They are easily fatigued by exertion and feel anxious and overwhelmed if ill or overworked.
- Thick, large, yellow scabs form on the occiput first and spread thence to face.
- Eruption mostly dry, but thick, bland pus under the crusts.
- Itching not very intense, but on awakening from sleep teething children are apt to scratch their head and make it bleed.
- Moist eruption upon legs, about navel and flexure of extremities; no dread of water, but eruptions are aggravated by water.
- Chronic eruption with cold feet, as it there were damp stockings on them; chalky stools; skin inclined to ulcerate. Eczema scrofulosum.[5]
Antimonium Crud:
- People likely to response to this remedy have eczema with thick, cracked skin and also prone to indigestion.
Suppurating, yellow-crusted eruption, pain to touch and easily detached.
- Green sanious pus oozes out from beneath the thick, hard, yellow crusts, irritating the surrounding parts, itching violently.
- Aggravation from poultices, bathing, working in water, from alcoholic drinks and in the sun.
- Gastric derangement with violent thirst and map tongue; especially on face and genital organs; impetigo scroti.[5]
Cantharis:
- Eczema Solare with Much Burning and Itching; when touched burning and smarting.
- Complications with urinary troubles; eruption begins in a small spot and spreads so as to involve a large surface, with a watery discharge underneath the scabs.
- Amelioration from lying down and in cool weather; Aggravation from warmth.
- All in all, Scales form on scalp like enormous dandruff; hair falls out; besides this, perspiration smells urinous; eruption mostly on right side.[5]
Graphitis:
- People likely to respond to this remedy have either tough or leathery skin with cracks and soreness and often have a long-term history of skin disorders.
- Furthermore, Eruptions cracked, moist, easily bleeding.
- Eczema of lids, eruptions moist also fissured.
- Dry, rough skin that breaks easily also exudes gluey moisture.
- Either Moist eczema or eruptions behind ears.
- Moist eczema around mouth also chin.
- Eczema oozing glutinous fluid which is watery also transparent.
- Such fluid may be thick, honey-like. Lastly, Very dry skin; never perspires.[6]
Hepar sulph:
- Basically, It spreading by means of new pimples appearing just behind the original affected parts.
- Violent itching.
- Sticking or pricking felt especially; on the parts, which may be painful to touch.[6]
Mezereum:
- A person who needs this remedy often has strong anxiety, felt physically in the stomach.
- It affects, especially, those parts of the skin that are normally deficient in fat.
- With intolerable itching, worse in bed and from touch; copious serous exudation.
- Eczema also itching eruptions after vaccination.
- In detail; The head is covered with thick leather-like crust under which pus collects here and there and the hair is glued together.
- Child scratches face incessantly; then it becomes covered with blood: inflammatory redness of face.
- Besides this; Craving for fat and a tendency to feel better in open air.
- Face becomes covered with a scab which the child constantly tears off anew, leaving raw spots on which fat pustules form.
- Lastly, Ichor excoriates other parts. [6]
Rhus tox:
- A person whose eczema has blister like eruptions that look red and swollen, itch intensely and are soothed by hot applications.
- Moist eruptions on head, beginning with small yellow vesicles with red areolae, forming thick crusts and hard horny scabs which eat off the hair, offensive itching, worse at night.
- Surface raw, excoriated, extends to shoulders or eczema scroti on insides of thighs.
- Discharging freely, or thickened, infiltrated and between the fields sore and humid.
- Aggravation by changes of weather, especially wet weather, in winter.
- Eczema of right hand.
- Cold fresh air is not tolerated on head making scalp painful.[5]
Sulphur:
- Dry, offensive, scabby, easily-bleeding, burning eruption, beginning along margin of hair from ear to ear posteriorly, with sore pain and cracks.
- Offensive with thick pus; yellow crusts, itching and burning, painful especially around chin and under the toes.
- Colicky babies with dry roughness of the skin of body, which itches from warmth and feels good from scratching.
- Soreness between nates and in groins, most comfortable when dirty, hates to be washed in fresh air.
- Amelioration from scratching or humid.[5]