Basically, Pituitary corticotrope adenomas account for 70% of patients with endogenous causes of Cushing’s syndrome.
However, it should be emphasized that iatrogenic hypercortisolism is the most common cause of cushingoid features.[1]
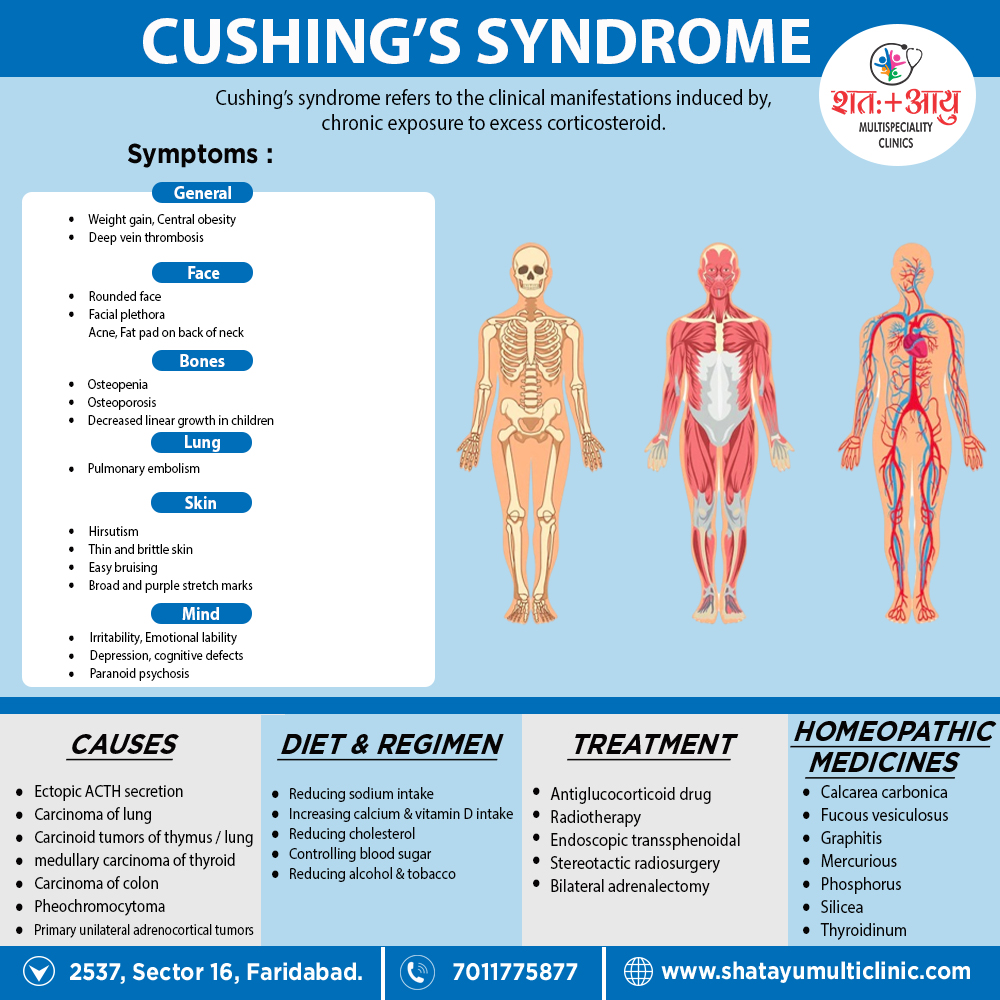
Cushing’s syndrome refers to the clinical manifestations induced by, chronic exposure to excess corticosteroid. [1]
Basically, Pituitary corticotrope adenomas account for 70% of patients with endogenous causes of Cushing’s syndrome.
However, it should be emphasized that iatrogenic hypercortisolism is the most common cause of cushingoid features.[1]
1.Firstly, ACTH excess i.e.: –
2.Secondly, Non-ACT dependent i.e.: –
3. Thirdly, ACTH – independent i.e.: –
| Body compartment/system | Signs and symptoms
|
| Body fat – | Weight gain, central obesity, rounded face, fat pad on back of neck (in other words, “buffalo hump”) |
| Skin – | Facial plethora, thin also brittle skin, easy bruising, broad also purple stretch marks, acne, hirsutism |
| Bone – | Osteopenia, osteoporosis (especially, vertebral fractures), decreased linear growth in children |
| Muscle – | Weakness, proximal myopathy(prominent atrophy of gluteal also upper leg muscles) either with difficulty climbing stairs or getting up from a chair |
| Cardiovascular system – | Hypertension, hypokalemia, edema, additionally atherosclerosis |
| Metabolism – | Glucose intolerance/diabetes, dyslipidemia |
| Reproductive system – | Decreased libido, in women amenorrhea (due to cortisol-mediated inhibition of gonadotropin release) |
| Central nervous system – | Irritability, emotional lability, depression, sometimes cognitive defects; occasionally, in severe cases, paranoid psychosis |
| Blood and immune system – | Increased susceptibility to infections, increased white blood cell count, eosinopenia, hypercoagulation with increased risk of deep vein thrombosis also pulmonary embolism. |
[1]
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. Now a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improve with homeopathic medicines.
Medicine for Cushing’s Syndrome:
Cushing’s syndrome refers to the clinical manifestations induced by, chronic exposure to excess corticosteroid.
References: