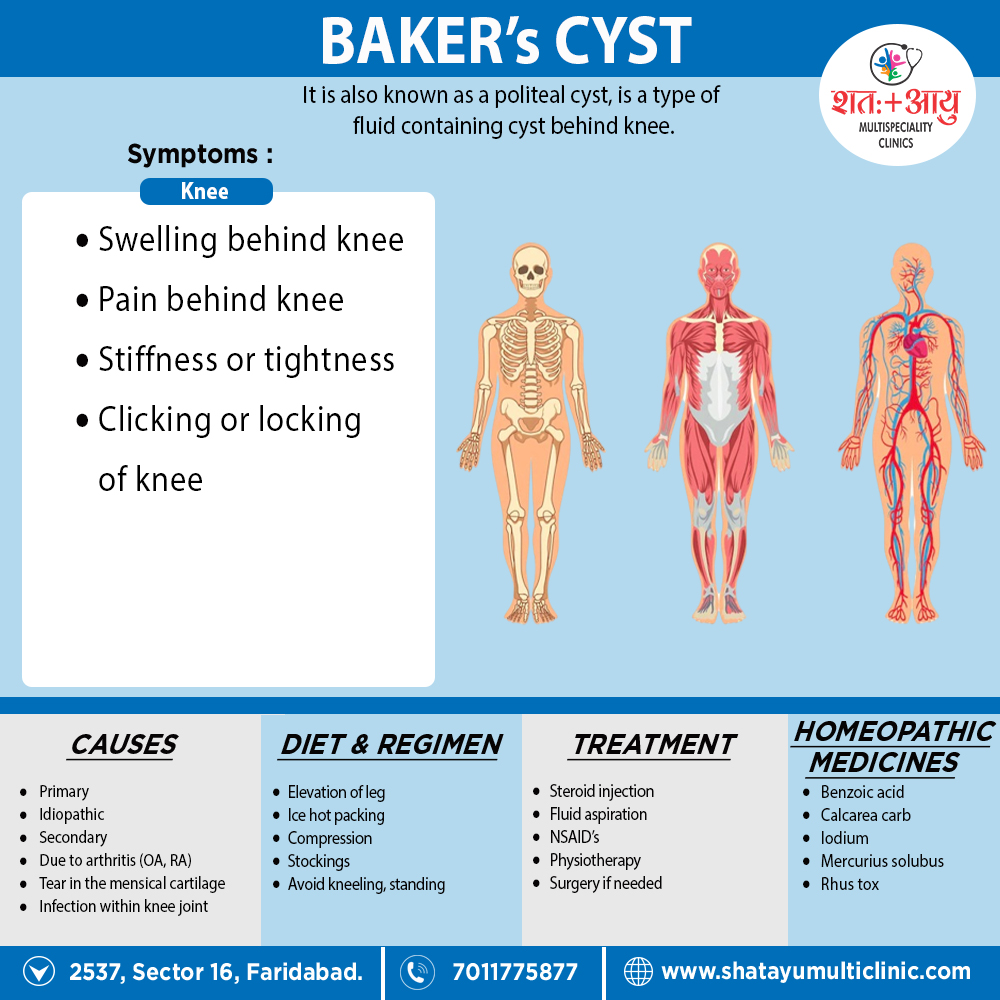
Homeopathic Treatment of Baker’s cyst:
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Bakers cyst:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines are selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis, which includes the medical history of the patient, physical and mental constitution, family history, presenting symptoms, underlying pathology, possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) is also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions. A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease is not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness are also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology is not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can be greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
The homeopathic remedies (medicines)
given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications are also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Benzoic acid
- Well indicated medicine for baker cyst. Benzoic Acid is a medicine used to treat a swollen knee due to gout.
- Along with swelling, painful nodes on the knee joint may be present.
- Gouty deposits of joints.
- Pain and swelling in knees.
- Drawing pain in the knees, a cracking sound upon movement also aggravation of the symptoms might indicate the need for this medicine.
- Bunion of great toe.
- Tearing pain in great toe.
- There are cracking sounds in joints on motion.
Calcarea flour
- Well indicated medicine either for ganglia or encysted tumors at the back of the wrist and popliteal fossa.
- Gouty enlargements of the joints.
- Chronic synovitis of knee joint.
Iodum
- Joints inflamed also painful.
- Pain in knee joints at night.
- There occurs white swelling of joints.
- Specifically for acrid sweat from feet.
- Well indicated medicine for baker cyst.
Silicea
- Well indicated medicine for baker cyst.
- Silicea is a natural medicine for housemaid’s knee also swelling when knee pains are tearing in nature.
- Pressure and exercise worsen the pain over the knee.
- The knee is also highly swollen and shining.
- Pain in knee, as if tightly bound, Pain beneath toes.
- Calves are tense also contracted.
- Loss of power in legs.
Mercurius solubis
- Well indicated medicine for baker cyst in knees.
- Contraction of legs and cramps in calves of legs
- There occur dropsical swelling of legs.
- There is great weakness, heaviness and painful weariness in thighs and legs.