Homeopathic Treatment of Asphyxia Neonatorum
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
Which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. Now a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improve with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Asphyxia Neonatorum:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy, potency and repetition of dose by Homeopathic doctor.
So, here we describe homeopathic medicine only for reference and education purpose. Do not take medicines without consulting registered homeopathic doctor (BHMS or M.D. Homeopath).
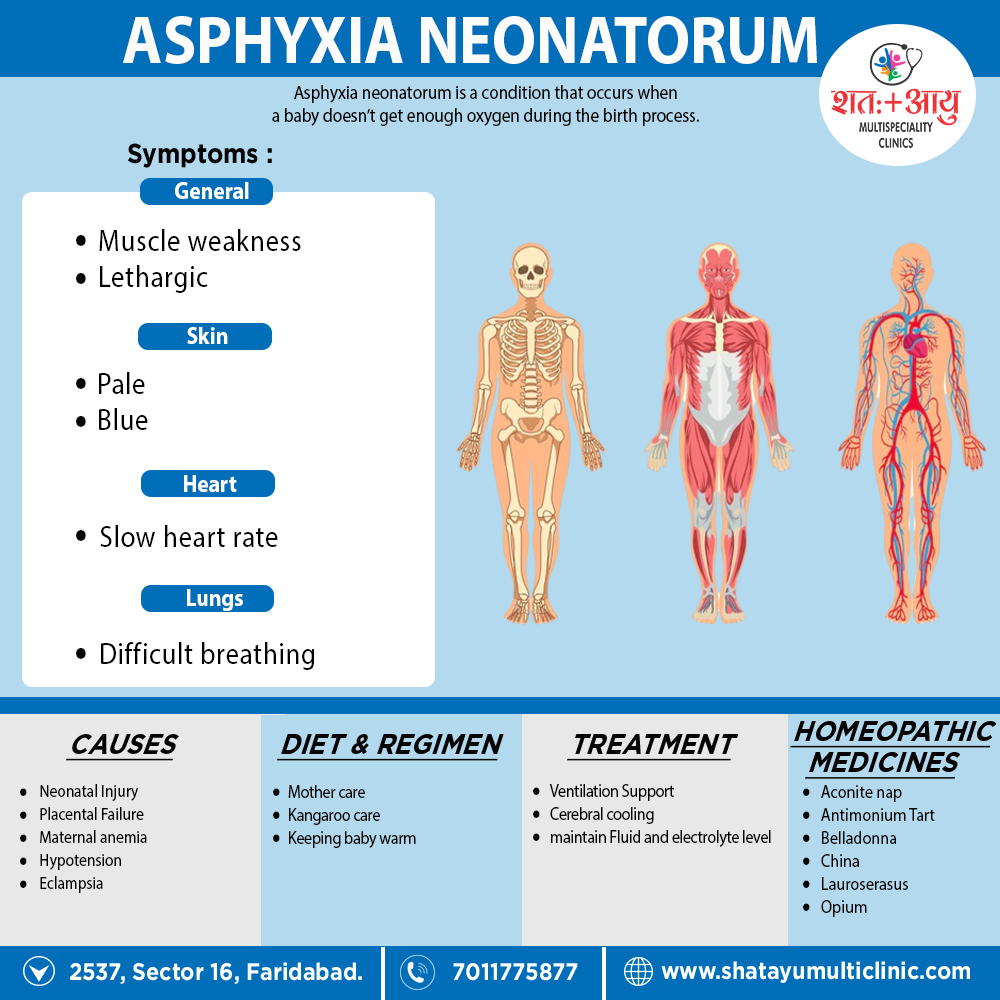
Aconite nap
Especially medicines for Asphyxia neonatorum. Apoplectic from, the babe is hot, purple-hued, pulseless also breathless, or nearly so.[2]
Antimonium Tart
Suffocative form; rattling of mucus in throat; child pale and breathless, although the cord still pulsates.
Belladonna
Apoplectic form; face very red, eyeballs injected, pupils dilated.
China
Syncope, after profuse hemorrhage
Lauroserasus
Face blue, with gasping for breath also nearly imperceptible breathing; twitching of muscles of the face.
Opium
Pale and breathless, cord still pulsates.[2]