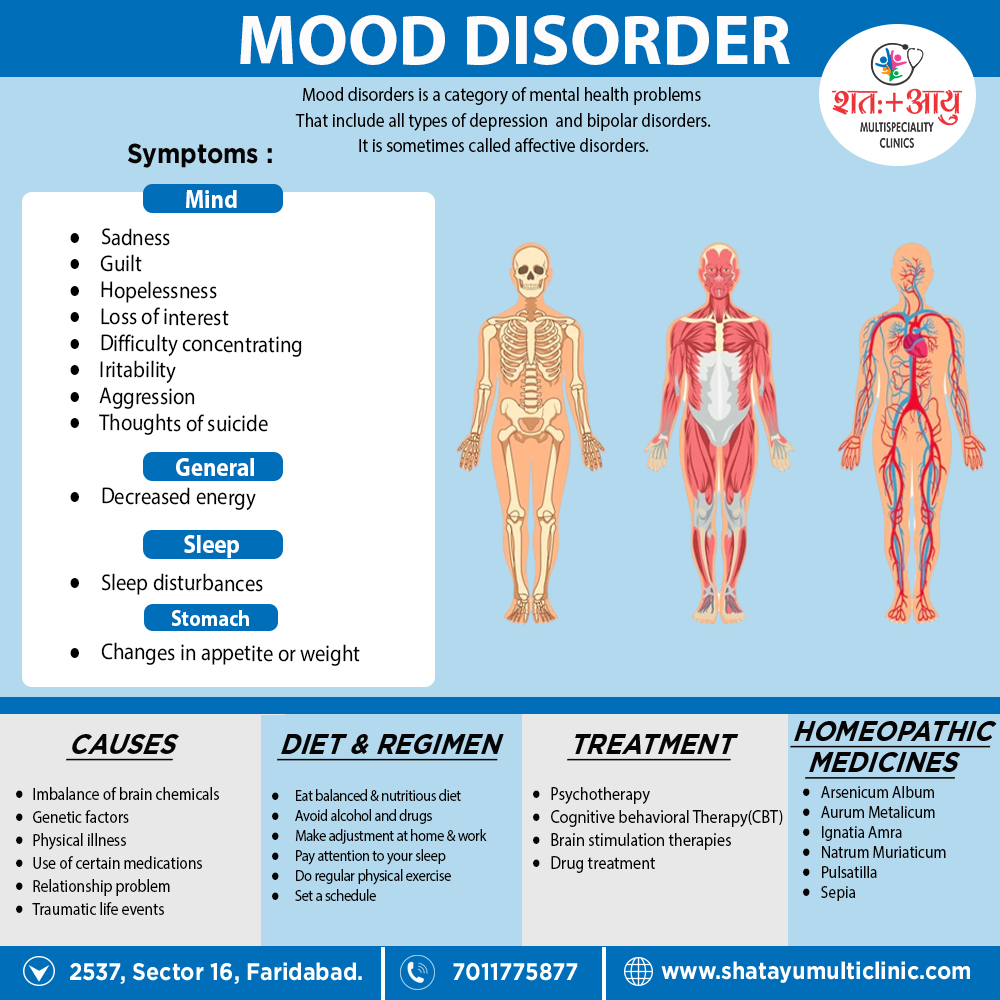
1. Arsenicum album :
Anxious, insecure, and perfectionist people who need this remedy may set high standards for themselves and others and become depressed if their expectations are not met. Worry about material security sometimes borders on despair. When feeling ill, these people can be demanding and dependent, even suspicious of others, fearing their condition could be serious.
2. Aurum metallicum:
Generally, This remedy can be helpful to serious people, strongly focused on work and achievement, which become depressed if they feel they have failed in some way. Additionally, Discouragement, self-reproach, humiliation, and anger can lead to “feelings of emptiness and worthlessness. All in all, The person may feel worse at night, with nightmares or insomnia.
3. Calcarea carbonica:
A dependable, industrious person who becomes overwhelmed from too much worry, work, or physical illness may benefit from this remedy. Moreover, Anxiety, fatigue, confusion, discouragement, self-pity, and a dread of disaster may develop. Lastly, A person who needs this remedy often feels chilly and sluggish and easily tires on exertion.
4. Causticum:
A person who feels depressed because of grief also loss ( either recent or over time) may benefit from this remedy. Furthermore, Frequent crying or a feeling of mental dullness and forgetfulness (with anxious checking to see if the door is locked, if the stove is off, etc.) are other indications. In detail, People who need this remedy are often deeply sympathetic toward others and, having a strong sense of justice, can be deeply discouraged or angry about the world.
5. Cimicifuga:
A person who needs this remedy can be energetic and talkative when feeling well, but upset and gloomy when depressed-with exaggerated fears (of insanity, of being attacked, of disaster). Painful menstrual periods and headaches that involve the neck are often seen when this remedy is needed.
6. Ignatia amara:
Sensitive people who suffer grief or disappointment and try to keep the hurt inside may benefit from this remedy. Wanting not to cry or appear too vulnerable to others, they may seem guarded, defensive, and moody. They may also burst out laughing, or into tears, for no apparent reason. A feeling of a lump in the throat and heaviness in the chest with frequent sighing or yawning are strong indications for Ignatia. Insomnia ( or excessive sleeping), headaches, and cramping pains in the abdomen and back are also often seen.
7. Kali phosphoricum:
If a person feels depressed after working too hard, being physically ill, or going through prolonged emotional stress or excitement, this remedy can be helpful. Exhausted, nervous, and jumpy, they may have difficulty in working or concentrating-and become discouraged and lose confidence. Headaches from mental effort, easy perspiration, and sensitivity to cold, anaemia, in- somnia, and indigestion often seen when this remedy is needed.
8. Natrum carbonicum:
Individuals who need this remedy are usually mild, gentle, and selfless- making an effort to be cheerful and helpful, and avoiding conflict whenever possible. After being hurt or disappointed, they can become depressed, but keep their feelings to themselves. Even when feeling lonely, they withdraw to rest or listen to sad music, which can isolate them even more, Nervous and physically sensitive (to sun, to weather changes, and to many food, especially milk), they may also get depress when feeling weak or ill.
9. Natrum muriaticum:
People who need this remedy seem reserved, responsible, and private yet have strong inner feelings (grief, romantic attachment, anger, or fear of misfortune) that they rarely show. Even though they want other people to feel for them, they can act affronted or angry if someone tries to console them, and need to be alone to cry. Anxiety, brooding about past grievances, migraines, back pain, and insomnia can also be experienced when the person is depressed. A craving for salt and tiredness from sun exposure are other indications for this remedy.
10. Pulsatilla:
People who need this remedy have a childlike softness and sensitivity-e-and can also be whiny, jealous, and moody. When depressed, they are sad and tearful, wanting a lot of attention and comforting. Crying, fresh air, also gentle exercise usually improve their mood. Besides this, Getting too warm or being in a . stuffy room can increase anxiety. Depression around the time of hormonal changes (puberty, either menstrual periods, or menopause) can often be helped with Pulsatilla.
11. Sepia:
People who feel weary, irritable, also indifferent to family members, and worn out by the demands of everyday life may respond to this remedy. Basically, They want to be left alone and may respond in an angry or cutting way if -anyone bothers them. They often feel better especially from crying, but would rather have others keep their distance and not try to console them or cheer them up. All in all, Menstrual problems, a sagging feeling in internal organs, sluggish digestion, and improvement from vigorous exercise are other indications for this remedy.
12. Staphysagria:
In general; Quiet, sensitive, emotional people who have difficulty standing up for themselves may benefit from this remedy. Hurt feelings, shame, resentment, also suppressed emotions can lead them to depression. If under too much pressure, they can sometimes lose their natural inhibition and fly into rages or throw things. Besides this, A person who needs this remedy may also have insomnia feeling sleepy all day, but unable to sleep at night), toothaches, headaches, stomach aches, or bladder infections that are stress-related.