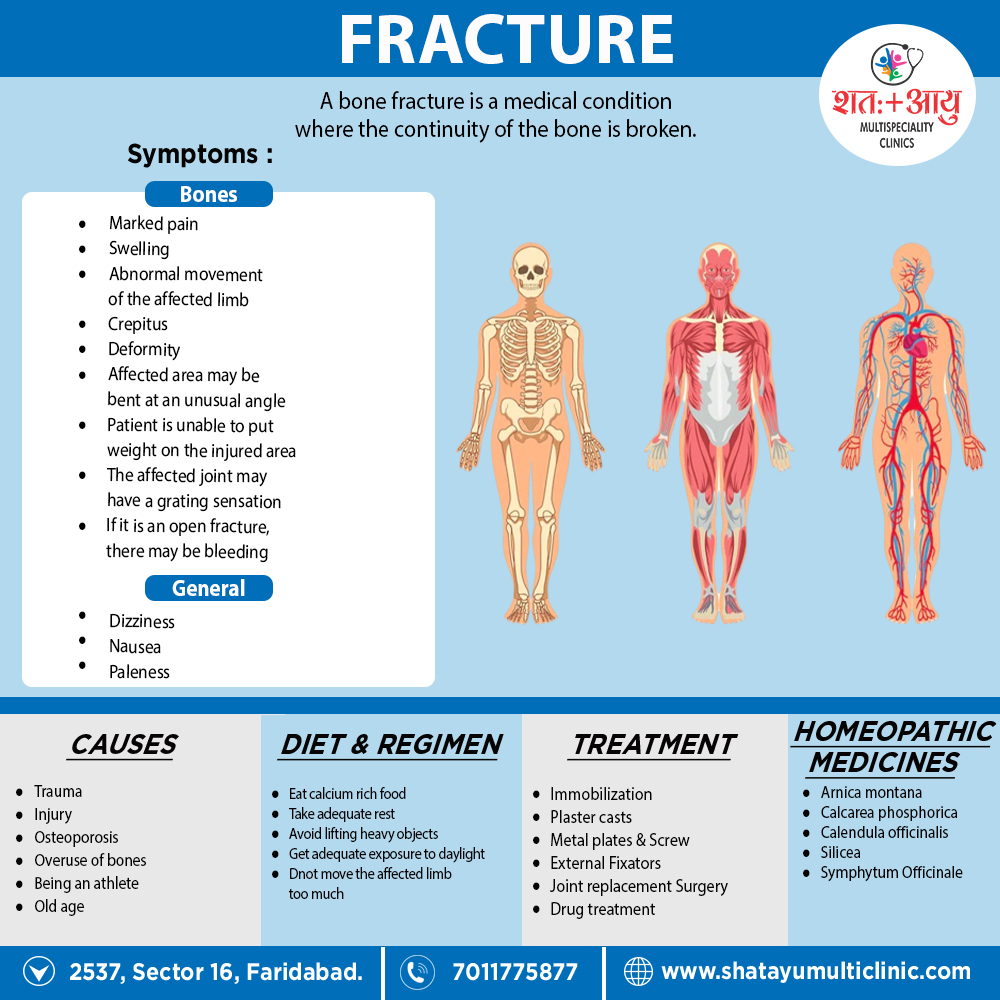
Management of fractures in the acute stage requires adequate pain relief, with opiates if necessary, reduction of the fractures to restore normal anatomy, and immobilisation of the affected limb to promote healing.
This can be achieved either by the use of an external cast or splint or by internal fixation.
Femoral neck fractures present a special management problem since nonunion and avascular necrosis are common.
This is especially true with intracapsular hip fractures, which should be treated by joint replacement surgery.
Following the fractures, rehabilitation is required with physiotherapy and a supervised exercise programme (this is especially important in older patients to prevent muscle wasting and loss of mobility).
Elderly patients with hip fractures also benefit from nutritional supplementation.
Patients with high energy and fatigue fractures generally require no further investigation or treatment once it has healed.
If the DEXA examination or other investigation shows evidence of osteoporosis or other metabolic bone disease, this should be treated appropriately. [1]
Immobilization:
This may include:
Plaster casts or plastic functional braces i.e.:
- These hold the bone in position until it has healed.
Metal plates and screws i.e.:
- In brief; Current procedures may use minimally invasive techniques.
Intramedullary nails i.e.:
- Internal metal rods are place down the center of long bones.
- Flexible wires may use in children.
External fixators i.e.:
- These may made of either metal or carbon fiber; they have steel pins that go into the bone directly through the skin.
- In detail, They are a type of scaffolding outside the body.
Usually, the fractured bone area is immobilize for 2-8 weeks.
The duration depends on which bone is affect and whether there are any complications, such as a blood supply problem or an infection. [2]