Homeopathic Treatment of Adenoids
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
Which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. Now a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improve with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Adenoids:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy, potency and repetition of dose by Homeopathic doctor.
So, here we describe homeopathic medicine only for reference and education purpose. Do not take medicines without consulting registered homeopathic doctor (BHMS or M.D. Homeopath).
Homeopathic Medicines for Adenoid i.e.:
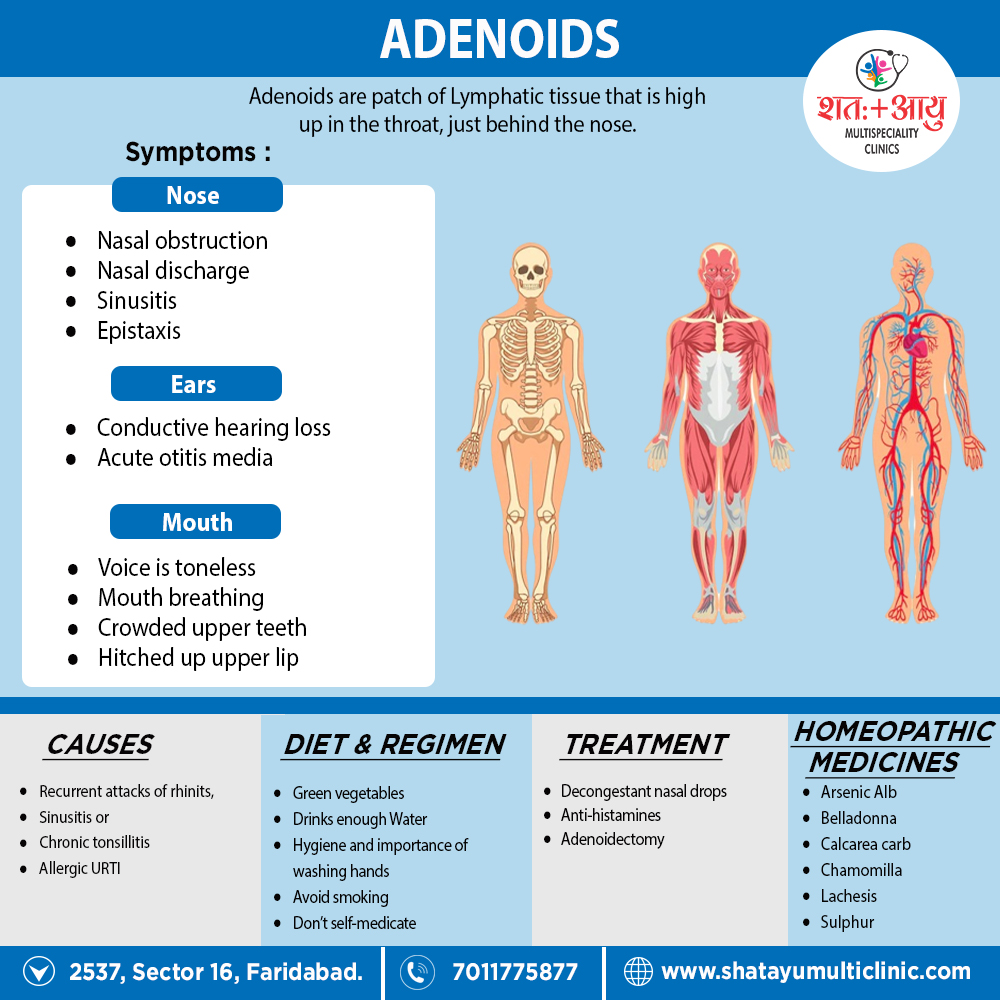
ARSENICUM ALBUM:
Swollen edematous, constricted burning, unable to swallow. additionally, thin watery excoriating discharge from nose. Sneezing. After that, Worse – wet weather after midnight from cold, cold drinks after food. seashore. right side. Better – heat, head elevated, also warm drinks.
BELLADONNA:
Dry as if glazed, angry looking congestion. Red < on right side. Most importantly, Tonsils enlarged, throat feels constricted, difficult deglutition, worse liquids, sensation of a lump. Moreover, Esophagus dry; feels contracted. Spasm in throat. Continual inclination to swallow. Scraping sensation. Muscles of deglutition very sensitive, otitis media with tearing pain in ear. Coryza, Worse – touch, noise, draught afternoon, lying down. On the other hand, Better – semi-erect.[2]
CHAMOMILLA:
Parotid and submaxillary glands swollen. Constriction and pain as from a plug. Furthermore, Earache with soreness, stitching pain. Irritable cough. Worse – by heat, open air, wind, night. whereas, Better – warm wet weather.[2]
CALCAREA CARBONICA:
Swelling of tonsils, and submaxillary glands, stitches on swallowing. Difficult swallowing. Particularly, Throbbing in ears with pulsating pain. Hardness of hearing. Nostrils sore and obstructed. Coryza Worse – from exertion, cold in every form. Water, moist air, washing, wet weather, standing, but Better by dry climate and weather, sneezing.
LACHESIS:
Sore throat, < left side – swallowing liquids. Dry intensely swollen, pain < by hot drinks, mucus sticks and cannot be forced up or down. Very painful < slightest pressure. Feel as if something is swelled also must be swallowed. Pain into ear – a tearing pain, sneezing and coryza. Worse – after sleep – left side, in the spring, warm bath, pressure or constriction, hot drinks. On the other hand, Better – warm applications.
MERCURIUS:
Bluish-red swelling. Constant desire to swallow. Putrid sore throat. Worse especially right side. In addition, Ulcers and inflammation. Stitches into ear on swallowing. Much sneezing. Worse – at night, wet weather, especially, lying on right side, perspiring, warm room and warm bed.
SULPHUR:
Throat has pressure as from a lump, splinter or a hair. Ball seems to rise also close pharynx, burning redness and dryness. Nose blocked, especially indoors for adenoids and polyps moreover worse – at rest, when standing, warmth in bed. On the other hand, Better – dry warm weather.[2]