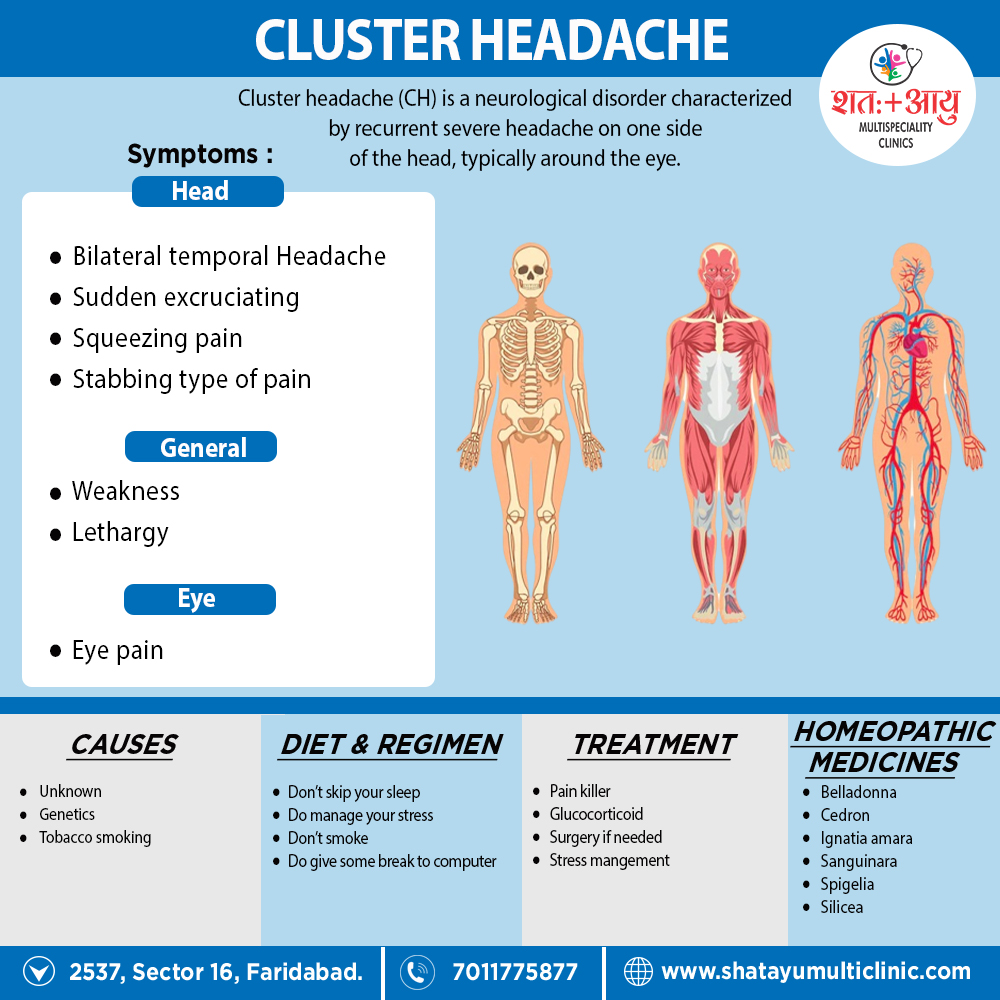
Homeopathic Treatment of Cluster Headache
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Cluster Headache:
Homoeopathic approach:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Medicine:
Cedron: Best Homeopathic medicine for Cluster Headache at precisely same hour
- Cedron is considered the top natural Homeopathic medicine that will provide immediate relief from Cluster Headaches.
- Cedron is of great help when the main symptom is severe pain around the eye at a particular hour.
- Periodicity in occurrence of periorbital pain is essentially marked. This pain may radiate into the ear.
- In other persons, the pain around the eye may radiate to the temples or back of head.
- Watering from eyes with burning may also present itself with eye pain.
- Night aggravation of pain is also noted. Although the pain may appear on any side, the pain over the left side of eye is felt more often for prescribing Homeopathic remedy Cedron.
Belladona: Homeopathic medicine for Cluster Headache with redness or swelling of eyes
- Belladona is the ideal natural Homeopathic medicine for Cluster Headache with redness or swelling of eyes and flushing of face.
- The characteristic feature for using this Homeopathic remedy is deep pain in the eyes, mostly throbbing or shooting in nature, with congestion and redness of eyes.
- The eyes also show protrusion.
- Photophobia i.e. intolerance to light or worsening of pain from light may also be noted.
- In most cases, lying down worsens the pain and tight bandage or pressure seems to provide relief.
- The sudden onset of a violent headache is also a marked feature.
- The attacks appear suddenly and with intensity and leave with the same suddenness.
Spigelia: Homeopathic medicine for left-side Cluster Headache
- Spigelia is a natural Homeopathic medicine which is very beneficial in treating the left-side Cluster Headache.
- Its use recommend when there is a severe violent pain around the eye and in the eye socket specifically on the left side. The eyeballs too appear large.
- The pain can be of varying nature like digging, boring, shooting, violent, throbbing or stitching pain, with a feeling of needles pricking in the eye on the left side.
- The main worsening factor given by a patient for using Homeopathic remedy Spigelia is pain in eye on moving or turning the eye.
- A few persons may also describe noise or touching the eye as the most aggravating factors.
- Rest in most cases seems to relieve the pain. Along with pain, redness of eyes with sensitivity to light and dropping of eyes also show their presence.
- Another marked feature for using Spigelia is occurrence of pain around the left eye in morning either on rising or while lying in bed.
- A characteristic relief from pain by washing with cold water is a peculiar symptom guiding the use of Homeopathic medicine Spigelia.
Sanguinaria Can: Right-side Cluster Headache
- For treating right-side Cluster Headache, natural Homeopathic medicine Sanguinaria Can is the ideal remedy.
- The use of Homeopathic medicine Sanguinaria Can consider in all those cases of Cluster Headache where the pain settles over or around the right eye.
- A bursting sensation with a feeling as if the eyes will be pressed out is very marked. Periodicity of pain note mostly with beginning of pain in morning and continuing till evening.
- The most aggravating factors in pain to kept in mind where Sanguinaria Can applicable are motion and light. And sleep and lying down still are the soothing factors.
- Characteristic relief from pain may also brought about by walking in open air for some patients needing Sanguinaria Can.
- Along with pain over right eye, there is a profuse watering of eyes. The eyes also very congested, and red with burning sensations.
- The face, especially cheeks, shows flushing. In a few persons, nasal congestion is a prominent feature.
Spigelia: Cluster Headache on left-side
- Spigelia is a top natural Homeopathic medicine for left-side cluster headache.
- In most cases, the person has a need to close the eye to get relief.
- Has marked elective affinity for the eye, heart, and nervous system.
- Neuralgia of the fifth nerve is very prominent in its effects. especially adapted to anaemic, debilitated, rheumatic, and scrofulous subjects. Stabbing pains. Heart affections and neuralgia.
- Very sensitive to touch, parts feel chilly, send shudder through frame.
- A remedy for stitches due to the presence of worms.
- Child refers to the navel as the most painful part.
- Semi-lateral, involving left eye; pain violent, throbbing; worse, making a false step. Pain as if a band around head.
Ignatia Amara – Effective for Cluster Headache With Stabbing Pain Deep In The Eyes
- Ignatia Amara a beneficial medicine use to treat a cluster headache when the person experiences stabbing pain deep in the eyes.
- A sensation of pressure in the eyes may also be felt. This attend with a sensation as if the eyes would fall out.
- Along with this, redness, flowing of tearing and burning in the eyes may also feel.
- The person needing Ignatia Amara suffers from a periodical headache that can occur every week, fortnight or every month.[3]